Flux 패턴이란?
View의 역할이 단순한 서버 사이드의 MVC 패턴과 달리, 프론트에서의 MVC 패턴은 View의 역할이 복잡하고 심지어는 View가 Model을 바꿔야 하는 일이 발생한다. 이를 해결하고자 Controller가 View와 Model의 중간에서 중개자 역할을 담당. 여기에서도 Controller가 지나치게 비대해지는 문제 발생한다.
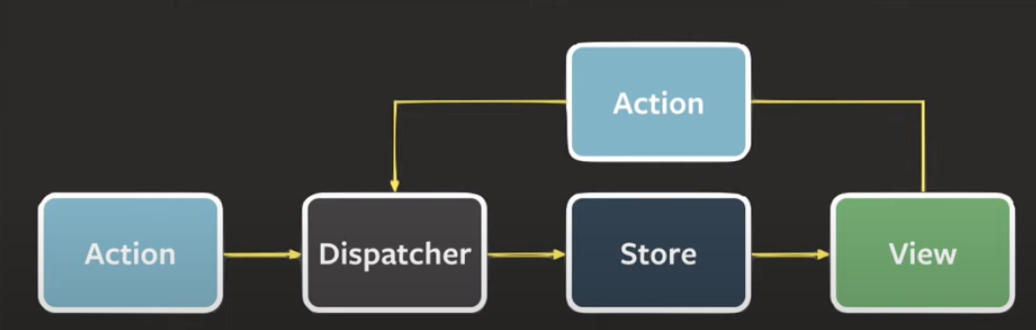
이를 해결하고자 나온 것이 Flux 패턴. View가 직접 Model(Store)를 조작하지 않고, Action을 통해 간접적으로 동작할 수 있게 한다. 위 사진에서 볼 수 있듯이 흐름이 단방향으로만 흐르게 만드는 것이 flux 패턴의 핵심.
각 항목의 역할
Action
상태 변경을 위한 정보를 담고 있는 객체. 종류를 나타내는 type, 변경해야 할 데이터를 담고 있는 payload라는 property들로 구성된다.
Dispatcher
dispath란 목적에 맞게 전송한다라는 뜻. Action을 전달받아 Action의 타입에 따라 Store의 변화를 일으킨다.
Store
상태를 저장하고 관리하는 역할을 담당한다.
View
UI 영역을 나타낸다.
Redux 라이브러리 뜯어보기
Flux 패턴으로 제작된 대표적인 라이브러리 redux의 코드를 살펴보도록 하자.
function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
var currentReducer = reducer
var currentState = preloadedState
var currentListeners = []
var nextListeners = currentListeners
var isDispatching = false
function getState() {
return currentState // 클로저로 currentState를 가져오고 있다.
}
function subscribe(listener) {
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error("Cannot subscribe when the reducer is executing.")
}
var isSubscribed = true
nextListeners.push(listener)
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed) {
return
}
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error("Cannot unsubscribe when the reducer is executing.")
}
isSubscribed = false
var index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener)
nextListeners.splice(index, 1)
currentListeners = null
}
}
function dispatch(action) {
if (isDispatching) {
// dispatching 하고 있으면 조기 리턴
throw new Error("The reducer is already executing.")
}
try {
isDispatching = true
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action)
} finally {
isDispatching = false
}
var listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners)
for (var i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
var listener = listeners[i]
listener()
}
return action
}
return {
dispatch: dispatch,
subscribe: subscribe,
getState: getState,
}
}
const initialState = { count: 0 }
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "INCREMENT":
return { count: state.count + 1 }
case "DECREMENT":
return { count: state.count - 1 }
default:
return state
}
}위 코드는 실제 redux의 createStore.js에서 가져온 스토어 생성 함수이다. 가볍게 쓸 목적이기 때문에 복잡한 검증 로직은 제외하고 가져왔다.
위 코드를 실행하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
const initialState = { count: 0 }
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "INCREMENT":
return { count: state.count + 1 }
case "DECREMENT":
return { count: state.count - 1 }
default:
return state
}
}
const store = createStore(counterReducer)
const store = createStore(counterReducer)
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log("Current state:", store.getState())
})
store.dispatch({ type: "INCREMENT" }) // Current state: { count: 1 }
store.dispatch({ type: "INCREMENT" }) // Current state: { count: 2 }
store.dispatch({ type: "DECREMENT" }) // Current state: { count: 1 }- store의 subscribe method를 호출하여 store의 변화를 감지하게 한다.
- dispatch method에 상태 변화(action)을 전달한다.
- dispatch가 일어나면 subscribe 되었던 listener(여기에서는 console.log… 부분) 들이 실행 된다.
위 코드에서 보면 createStore에 Observer Pattern이 사용되었음을 확인할 수 있다.
Observer Pattern
옵저버 패턴은 구독과 발행의 개념으로 표현된다.
function Click() {
this.handlers = [] // observers
}
Click.prototype = {
subscribe: function (fn) {
this.handlers.push(fn)
},
unsubscribe: function (fn) {
this.handlers = this.handlers.filter(function (item) {
if (item !== fn) {
return item
}
})
},
fire: function (o, thisObj) {
var scope = thisObj || window
this.handlers.forEach(function (item) {
item.call(scope, o)
})
},
}
function run() {
var clickHandler = function (item) {
console.log("fired: " + item)
}
var click = new Click()
click.subscribe(clickHandler)
click.fire("event #1")
click.unsubscribe(clickHandler)
click.fire("event #2")
click.subscribe(clickHandler)
click.fire("event #3")
}
run()- subscribe 함수를 실행하면 해당 프로퍼티를 handler에 담아둔다.
- unsubscribe 함수를 실행하면 해당 프로퍼티에 해당하는 handler를 삭제할 수 있다.
- fire 함수를 실행하면 handler 안에 들어있는 함수들이 실행된다.